E-Way Bill Under GST
RELEVANT SECTION AND RULES:-
Section 68:- Inspection of goods in movement.
Section 122:- Penalty for certain offences.
Section129:- Detention, Seizure and release of Goods and
Conveyance in transit.
Rule 138:- Information to be furnished prior to commencement of movement of goods and generation of e-way bill.
INTRODUCTION:-
During the pre GST period the goods consigned could have either
invoice or delivery challan or the prescribed challan under the respective VAT
or Sales Tax Act of the particular State. The goods which were consigned were
normally instructed to be verified by the outgoing and incoming check post of
that region. Because of this there used to be a huge delay in the movement of
goods and more time was wasted in the check post or with the roving squad
detentions, in case of improper documentation or for other purpose.
When the Goods and Services Tax was introduced by the Government,
one of its purpose was to make movement of goods easier and enable the business
to be carried on in a better way. Hence, in GST regime check posts were
abolished all over the country.
However, to have a check on the documentation of the movement of
goods, the Government introduced a way bill on the e-portal, which is nothing
but a delivery challan created in the e-portal. The portal provides an
identification number to the e-way bill (“EWB”).
The EWB contains the entire details of the consignment like Name,
Address and GSTIN of consignor and consignee. It also has the details of
commodity consigned, quantity consigned and value consigned. The details of
movement of goods is also mentioned in the e-way bill. The registered dealers
under GST can generate e-way bill as a supplier or as a recipient of the goods.
The Government vide Notification No.09/2018 – Central Tax dated
23.01.2018 notify www.ewaybillgst.gov.in
as the Common Goods and Services Tax Electronic Portal for furnishing the e-way
bill. This website will be managed by the National Informatics Centre, Ministry
of Electronics & Information Technology, Government of India. From
01.04.2018, the inter-State movement of goods for a value beyond Rs.50,000/-,
need to have the e-way bill. The assessee will have to look in to the movement
of goods whether inter-State or intra-State. When the movement is inter-State
or intra-State they have to follow the procedures of CGST & SGST Act and
for generation of EWB within the State, the threshold will be as per SGST Act.
BENEFITS OF E-WAY BILL:-
Cost reduction:- E-way bill reduces the logistics
cost. E-way bill has reinforced proper invoicing and thereby reduce tax
avoidance.
Efficient transportation:- It has enabled efficient and speedy
transportation. A truck in India covers an annual average distance of 85,000
kms as compared to 1,50,000 to 2,50,000 kms in developed countries which is a
clear indication that our transportation systems needs some reforms. E-way bill
would help to reform the transportation industry.
Waiting Time:- No waiting time at check post and
faster movement of goods resulting in the optimum use of vehicle/resources.
User friendly e-way bill system (“EWS”):- EWS and
portal are user friendly and easy; even dealers can easily download the e-way
bill.
Easy & Quick generation of EWB:- EWB
could be generated easily and quickly, there is not big task to generate EWB.
IMPORTANT TERMS:-
Transport:-
Movement or journey is part of transportation and it can be said
that transportation has commenced as soon as the consignor hands over the goods
with clear and irrevocable instructions to a carrier to put them on its journey
to a specified destination and hand them over to a specified (or altered)
consignee (or his order). Transportation will conclude only when the Handbook
on E-Way Bill under GST instructions of the consignor have been satisfactorily
carried out by the carrier by handing over the goods to the consignee (or his
order). E-way bill is required ‘before’ commencement of transportation
regardless of the time of commencement of the journey.
Movement of Goods:-
Transportation of goods within the State is called intra State
movement. The threshold limit to generate EWB mandatorily is as per the SGST
Rules. Similarly, transportation of goods outside the State is called as inter
State movement and it is mandatory to generate EWB if the consignment value exceeds
` 50,000/-.
E.G.:- Assume Transportation of goods for a
consignment value of ` 65,000/- from the place of business of Mr. A in Chennai,
Tamil Nadu to the place of business of Mr. B in Chennai, which is a unit
located in the Special Economic Zone. The nature of supply for the above
transaction as per Section 7 of IGST Act, 2017 will be inter-State supply.
However, the movement of goods is intra-State movement. The limit to generate
EWB in case of intra State movement is Rs.1,00,000/- as per TNGST Rules, 2017.
Hence, generation of EWB is not mandatory. Not all inter-State
supply results in inter State movement. Similarly, not all intra State supply
results in intra State movement. It must be noted that EWB has to be generated
based on the nature of movement of goods and on the consignment value.
Consignment Note:-
A consignment note is a document issued by a goods transportation
agency against the receipt of goods for the purpose of transporting the goods
by road in a goods carriage.
Consignment Value:-
The consignment value of goods shall be the value, determined in accordance
with the provisions of Section 15 of CGST Act, 2017, declared in a tax invoice,
a bill of supply or a delivery challan, as the case may be, issued in respect
of the said consignment and also includes the Central Tax, State or Union
Territory Tax, Integrated Tax and Cess charged, if any, in the document and
shall exclude the value of exempt supply of goods where the invoice is issued
in respect of both exempt and taxable supply of goods.
Place of Delivery:-
FORM GST EWB-01 requires the ‘place of delivery’ to be specified
and this expression ‘place of delivery’ must not be inter changed with ‘place
of supply’, which is a legal expression as determined by the tests laid down in
IGST Act. EWB is intended to create contemporaneous trail of physical movement
of the goods. It is not meant to address the legal concept of ‘place of supply’
which can vastly differ from ‘place of delivery’. Though physical movement of
the goods may be from one location to another, in the eyes of law, the place of
supply could be the location of the recipient. Hence it is not conceivable for
EWB to require information about the ‘place of supply’ but simply the ‘place of
delivery’ or ‘destination of journey’. In fact, it can be seen that, when GSTIN
of the recipient is incorporated, the place of delivery will auto-populate
within the EWB.
PENALTY (Section 122):-
As per section 122(1)(xiv) of CGST Act, 2017 penalty will be as
follow
Offence:- For transports any taxable goods without the
cover of documents.
Penalty:- Rs. 10,000/- each for CGST and SGST OR Tax
amount, Whichever is higher.
In Case of
Minor Error in Particulars in Part A of GST EWB-01 penalty will be Rs. 500/-
Each in CGST and SGST Act, 2017.
Section 68(1) of the CGST Act stipulates that the Government may
require the person in charge of a conveyance carrying any consignment of goods
of value exceeding Rupee fifty thousand (Rule 138) to carry with him
such documents and such devices as may be prescribed. And the same is
prescribed in Rule 138. In other words, the provisions relating to
implementation of e-way bill are contained in Section 68 of the CGST / SGST
Act, 2017 read with Rule 138 of the CGST Rules, 2017, for inter-State movement
of goods and Rule 138 of the respective SGST / UTGST Rule 2017, for intra-State
movement of goods.
As per Section 68(2) details of documents should be validated.
Section 68(3) require the person in charge of the said conveyance to produce the document and devices and also allow the inspection of goods.
GENERATION OF E-WAY BILL PRIOR TO COMMENCEMENT OF MOVEMENT OF
GOODS (RULE 138):-
Rule 138(1):-Every registered person who causes
movement of goods of consignment value exceeding fifty
thousand rupees needs to prepare E-way bill before commencement
of such movement for the following transactions.
·
In relation to a supply; or
·
For reasons other than supply; or
·
Due to inward supply from an unregistered
person.
From the above analysis it is clear that registered person needs
to prepare E-way bill even if the combined value of all the consignments are
more than fifty thousand rupees although value
of single consignment is less than fifty thousand
rupees.
However Registered person or transporter may at his option,
generate and carry the e-waybill even if the value of the consignment is less
than fifty thousand rupees. {First Proviso of rule 138(3)}
Proviso of sub rule (1):-
First Proviso:- Transporter
can generate can generate E-Way bill on authorisation received from registered
person.
Second Proviso:- E-Commerce operator or
Courier agencies can generate E-Way bill on authorisation received from consigner
if goods are transported through them.
Third Proviso:- where goods are sent by a principal located in
one State or Union territory to a job worker located in any other State or
Union territory, the e-way bill shall be generated either by the principal or
the job worker, if registered, irrespective of the value of the consignment. (E-Way bill is Compulsory irrespective of the value of the
consignment.)
Fourth Proviso:- where handicraft goods are transported
from one State or Union territory to another State or Union territory by a
person who has been exempted from the requirement of obtaining registration
under clauses (i) and (ii) of section 24 (i.e. Compulsory registration), the e-way
bill shall be generated by the said person irrespective of the value of the
consignment. (E-Way bill is Compulsory irrespective
of the value of the consignment.)
Handicraft Goods:- As per Explanation of Notification
No. 21/2018 -Central Tax (Rate)_Dt. 26.07.2018 “handicraft goods “means Goods
predominantly made by
hand even though
some tools or
machinery may also
have been used in
the process; such
goods are graced
with visual appeal
in the nature
of ornamentation or in-lay work or some similar work of a substantial
nature; possess distinctive features, which can be aesthetic, artistic, ethnic
or culturally attached and are amply different from mechanically produced goods
of similar utility.
Compulsory Registration (Section 24):-
Clause (i):- Persons making any inter-State taxable
supply
However Notification No. 03/2018 IT, Dt. 22.10.2018 specifies the
persons, who engaged in inter-State taxable supplies of handicraft goods as
defined in the “Explanation” in notification No. 21/2018 CTR, Dt. 26.07.2018
and notification No. 03/2018 IT, Dt.
22.10.2018 and notification No. 09/2017 IT, Dt. 13.10.2017, shall be exempted
from obtaining registration under the said Act provided aggregate turnover, to
be computed on all India basis, not exceeding threshold limit in a financial
year.
Such persons making
inter-State taxable supplies of handicraft goods mentioned in the preceding
paragraph shall be required to obtain a Permanent Account Number and generate
an e-way bill in accordance with the provisions of rule 138 of the Central
Goods and Services Tax Rules, 2017.
Clause (ii):- Casual taxable persons making taxable
supply
However Notification 32/2017 CT Dt. 15.09.2017 hereby specifies
the casual taxable persons making taxable supplies of handicraft goods shall be
exempted from obtaining registration under the aforesaid Act provided aggregate
turnover, to be computed on all India basis, not exceeding threshold limit in a
financial year.
The casual taxable persons
mentioned in the preceding paragraph shall obtain a Permanent Account Number
and generate an e-way bill in accordance with the provisions of rule 138 of the
Central Goods and Services Tax Rules, 2017.
The above exemption shall
be available to such persons who are making inter-State taxable supplies of
handicraft goods and are availing the benefit of notification No. 03/2018 IT,
Dt. 22.10.2018.
Parts of E-Way Bill:-
Part A:- Part “A” Contain particulars related to
consigner, consigner, goods.
Part B:- Part “B” Contain particulars related to type
of transport (i.e. by Road, Rail, Air, Vessel etc.)
ANALYSIS OF APPLICABILITY OF E-WAY BILL:-
EWB is not required for all transactions undertaken by a taxable
person. EWB is required for all transactions involving movement of goods only
whether by way of a supply or not. EWS is required in transactions involving
goods but ‘treated as’ supply of services such as leasing of goods or delivery
of food drink. In other words, every time there is movement of goods, whether
by way of supply of goods or supply of services, EWB will be required. Goods
supplied and goods involved in the supply of services will require EWB as these
involve movement of goods. But goods consumed in supply of services which does
not involve movement, do not require EWB.
GENERATION OF E-WAY BILL:-
E-Way bill shall be generate, in Form
of FORM GST EWB-01, only after furnishing the information in Part B of FORM GST EWB-01 if goods
are moving by road (i.e. Own conveyance or a hired one or a public
conveyance).
The e-way bill shall not be valid for
movement of goods by road unless the information in Part-B of FORM GST
EWB-01 has been furnished except in the case of movements covered under the
third proviso to sub-rule (3) and the proviso to sub-rule (5).
If goods are moving by railways or by air
or vessel E-Way bill shall be generated in
Form of FORM GST EWB-01 even if the information in Part B of FORM
GST EWB-01 furnished after commencement of movement.
However, Where the goods are transported for a distance of up to fifty kilometres within the State or Union territory from the
place of business of the consignor to the place of business of the transporter
for further transportation, the supplier or the recipient, or as the
case may be, the transporter may Not furnish the details of conveyance in Part B of FORM GST EWB-01. {Third Proviso of rule
138(3)}
Further where the goods are transported for a distance of up to fifty kilometres within the State or Union territory from the
place of business of the transporter finally to the place of business of the
consignee, the details of the conveyance may not be updated in the e-way
bill. {Proviso of rule 138(5)}
Where the goods are transferred from
one conveyance to another, the consignor or the recipient, who has
provided information in Part A of the FORM GST EWB-01 , or the transporter
shall, before such transfer and further movement of goods, update the details
of conveyance in the e-way bill on the common portal in Part B of FORM GST
EWB-01.
Upon generation of the e-way bill on the common portal, a unique
e-way bill number (EBN) shall be made available to the supplier, the recipient
and the transporter on the common portal and the unique number so generated
shall be valid for a period of fifteen days for
updation of Part B of FORM GST EWB-01.
The information furnished in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 shall be
made available to the registered supplier on the common portal who may utilize
the same for furnishing the details in FORM GSTR-1.
Provided that when the information has been furnished by an
unregistered supplier or an unregistered recipient in FORM GST EWB-01 , he
shall be informed electronically, if the mobile number or the e-mail is
available.
WHO CAN GENERATE E-WAY BILL:-
·
Registered person or
·
Un-Registered person (However goods are supply
to registered person then the movement shall be said to be caused by such
recipient if the recipient is known at the time of commencement of the movement
of goods) or
·
Transporter
Where the consignor or the consignee has Not generated the e-way
bill in FORMGST EWB-01 and the aggregate of the consignment value of goods
carried in the conveyance is more than fifty thousand rupees, the transporter,
except in case of transportation of goods by railways, air and vessel, shall,
in respect of inter-State supply, generate the e-way bill in FORM GST EWB-01 on
the basis of invoice or bill of supply or delivery challan, as the case may be,
and may also generate a consolidated e-way bill in FORM GST EWB-02 on
the common portal prior to the movement of goods. {Rule 138(7)}
Provided that where the goods to be transported are
supplied through an e-commerce operator or a courier agency, the information in
Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 may be furnished by such e-commerce operator or
courier agency.
CANCELLATION OF E-WAY BILL:-
Where an e-way bill has been generated under this rule , but goods
are either not transported or are not transported as per the details furnished
in the e-waybill, the e-way bill may be cancelled electronically on the common
portal within twenty four hours of
generation of the e-way bill.
Provided that an e-way bill cannot
be cancelled if it has been verified in transit
in accordance with the provisions of rule 138B.
Provided that where, under circumstances of an exceptional nature,
including trans-shipment, the goods cannot be transported within the validity
period of the e-way bill, the transporter may extend the validity period after
updating the details in Part B of FORM GST EWB-01 , if required.
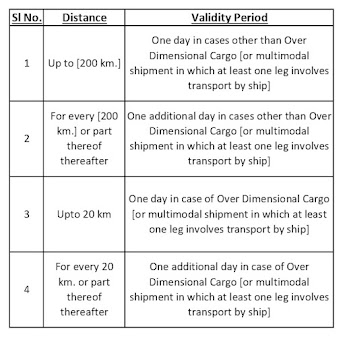
Provided also that the validity of the e-way bill may be extended within eight hours from the time of its expiry.
“Over dimensional cargo” means a
cargo carried as a single indivisible unit and which exceeds the dimensional
limits prescribed in Rule 93 of the Central Motor Vehicle Rules, 1989, made
under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988, or in simple terms it
means vehicles carrying cars of fuel falling in the category of over
dimensional units of conveyance have to move very slow as compared to other
vehicles.
COMMUNICATION OF GENERATION OF E-WAY BILL:-
The details of the e-way bill generated under this rule shall be
made available to the,
·
Supplier, if registered, where the information
in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 has been furnished by the recipient or the
transporter; or
·
Recipient, if registered, where the
information in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 has been furnished by the supplier or
the transporter, on the common portal.
And the supplier or the recipient, as the case may be, shall
communicate his acceptance or rejection of the consignment covered by the e-way
bill.
Where the person to whom the information specified above has been
made available does Not communicate his acceptance or rejection within seventy two hours of the details being made available to him
on the common portal, or the time of delivery of goods
whichever is earlier, it shall be deemed that he has accepted the said
details.
CASES WHERE NO E-WAY BILL IS REQUIRED {RULE 138(14)}:-
·
Where the goods being transported are
specified in Annexure.
|
Sr. No. |
Description
of Goods |
|
1 |
Liquefied petroleum gas for supply to household
and Non domestic exempted category (NDEC) customers |
|
2 |
Kerosene oil sold under PDS (Public Distribution
System) |
|
3 |
Postal baggage transported by Department of Posts |
|
4 |
Natural or cultured pearls and precious or
semi-precious stones; precious metals and metals clad with precious metal
(Chapter 71) |
|
5 |
Jewellery, goldsmiths' and silversmiths' wares
and other articles (Chapter 71) [excepting Imitation Jewellery (7117)] |
|
6 |
Currency |
|
7 |
Used personal and household effects |
|
8 |
Coral, unworked (0508) and worked coral (9601) |
·
Where the goods are being transported by a
Non-motorised conveyance.
MOTOR
VEHICLES: -
As per Section 2(76) of CGST Act, 2017
Motor vehicle shall have the same meaning as assigned to it in clause (28) of
section 2 of the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988.
As per Section 2(28) of the Motor
Vehicles Act, 1988 Motor Vehicles or Vehicles means any mechanically propelled
vehicle adapted for use upon roads whether the power of propulsion is
transmitted thereto from an external or internal source and includes a chassis
to which a body has not been attached and a trailer; but does not include a
vehicle running upon fixed rails or a vehicle of a special type adapted for use
only in a factory or in any other enclosed premises or a vehicle having less
than four wheels fitted with engine capacity of not exceeding twenty-five cubic
centimetres.
|
Motor
Vehicles (Those which are used upon Road) |
|||||||||
|
Includes |
Exclude |
||||||||
|
1) Four Wheelers or More |
1) Three Wheelers of less having
engine capacity <25CC |
||||||||
|
2) Three Wheelers or Less having
Engine Capacity >25CC |
2) Rail |
||||||||
|
3) Chassis (Frame) |
3) Specifically used in factory or
enclosed premises |
||||||||
·
Where the goods are being transported from the
customs port, airport, air cargo complex and land customs station to an inland
container depot or a container freight station for clearance by Customs.
·
In respect of movement of goods within such
areas as are Notified under clause (d) of sub-rule (14) of rule 138 of the
State or Union territory Goods and Services Tax Rules in that particular State
or Union territory.
·
Where the goods, other than de-oiled cake,
being transported, are specified in the Schedule appended to Notification No. 2/2017-
Central tax (Rate) dated the 28th June, 2017 published in the Gazette of India,
Extraordinary, Part II, Section 3 , Sub-section (i), vide number G.S.R 674 (E)
dated the 28th June, 2017 as amended from time to time. (Basically Exempted Goods)
·
Where the goods being transported are
alcoholic liquor for human consumption, petroleum crude, high speed diesel,
motor spirit (commonly known as petrol), natural gas or aviation turbine fuel. (Non GST Items)
·
Where the supply of goods being transported is
treated as No supply under Schedule III of the Act.
SCHEDULE III:- ACTIVITIES OR TRANSACTIONS WHICH SHALL BE TREATED NEITHER AS A SUPPLY OF GOODS NOR A SUPPLY OF SERVICES.
1.
Services by an employee to the employer in the course of or in relation to his
employment.
2.
Services by any court or Tribunal established under any law for the time being
in force.
3.
(a) the functions performed by the Members of Parliament, Members of State
Legislature, Members of Panchayats, Members of Municipalities and Members of
other local authorities;
(b) The duties performed by any person who
holds any post in pursuance of the provisions of the Constitution in that
capacity; or
(c) the duties performed by any person as a
Chairperson or a Member or a Director in a body established by the Central
Government or a State Government or local authority and who is not deemed as an
employee before the commencement of
this clause.
4.
Services of funeral, burial, crematorium or mortuary including transportation
of the deceased.
5.
Sale of land and, subject to clause (b) of paragraph 5 of Schedule II, sale of
building.
6.
Actionable claims, other than lottery, betting and gambling.
7.
Supply of goods from a place in the non-taxable territory to another place in
the non-taxable territory without such goods entering into India.
8.
(a) Supply of warehoused goods to any person before clearance for home
consumption;
(b) Supply of goods by the consignee to any
other person, by endorsement of documents of title to the goods, after the
goods have been dispatched from the port of origin located outside India but
before clearance for home consumption.
·
Where the goods are being transported,
1.
Under customs bond from an inland container
depot or a container freight station to a custom sport, airport, air cargo
complex and land customs station, or from one customs station or customs port
to another customs station or customs port, or
2.
Under customs supervision or under customs
seal.
·
Where the goods being transported are transit
cargo from or to Nepal or Bhutan.
· Where the goods being transported are exempt from tax under Notification No 7/2017-Central Tax(Rate) , dated 28th June 2017 published in the Gazette of India, Extraordinary, Part II, Section 3 , Sub-section (i), vide number G.S.R 679(E)dated the 28th June, 2017 as amended from time to time and Notification No 26/2017 Central Tax(Rate) , dated the 21st September, 2017 published in the Gazette of India, Extraordinary, Part II, Section 3 , Sub-section (i), vide number G.S.R 1181(E)dated the 21st September, 2017 as amended from time to time.
Following Supplies are notifying in
Notification No. 7/2017-Central Tax (Rate), Dated 28th June 2017.
1.
The supply of goods by the CSD (Canteen Stores
Department) to the Unit Run Canteens.
2.
The supply of goods by the CSD (Canteen Stores
Department) to the authorized customers.
3.
The
supply of goods
by the Unit Run
Canteens to the
authorized customers.
·
Any movement of goods caused by defence
formation under Ministry of defence as a consignor or consignee.
·
Where the consignor of goods is the Central
Government, Government of any State or a local authority for transport of goods
by rail.
·
Where empty cargo containers are being
transported.
·
Where the goods are being transported up to a
distance of twenty kilometres from the place of the business of the consignor to
a weighbridge for weighment or from the weighbridge back to the place of the
business of the said consignor subject to the condition that the movement of
goods is accompanied by a delivery challan issued in accordance with rule 55 .
·
Where empty cylinders for packing of liquefied
petroleum gas are being moved for reasons other than supply.
REQUIREMENT OF DOCUMENTS TO BE HAVE WITH TRANSPORT OF GOODS (Rule
138A):-
1.
Tax Invoice or Bill of supply or Delivery
Challan.
2.
Copy of E-Way Bill. (However E-way bill is not required to be carry with in case of movement
of goods by rail or by air or vessel).
In case of imported goods, the person
in charge of a conveyance shall also carry a copy of the bill of entry filed by
the importer of such goods and shall indicate the number and date of the bill
of entry in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01.
In case of E-Invoice, the Quick
Response (QR)code having an embedded Invoice Reference Number (IRN) in it, may
be produced electronically, for verification by the proper officer in lieu of the
physical copy of such tax invoice.
VERIFICATION OF DOCUMENTS AND
CONVEYANCES (Rule 138B):-
Who Can verify:-
Commissioner or Officer empowered by him.
What is to be verify:- E-Way bill
in Physical or Electronic Form for all Inter-State or Intra-State Movement of
Goods.
Physical verification of Conveyance:- On
receipt of specific information on evasion of tax.
INSPECTION AND VERIFICATION OF GOODS
(Rule 138C):-
Report of Verification of Goods:-
1.
Summary Report:- Part
A of FORM GST EWB-03 (Within 24 Hrs. of Inspection)
2.
Final Report:- Part
B of FORM GST EWB-03 (Within 3 Days of such Inspection) {3 Days time may be further
extended for further period of not exceeding 3 Days)
No Further Verification of Goods if once
done unless and until have information relating to evasion of tax.
Where a vehicle has been intercepted
and detained for a period exceeding thirty minutes,
the transporter may upload the said information in FORM
GST EWB-04 on the common portal.
RESTRICTION ON FURNISHING OF
INFORMATION IN PART A OF FORM GST EWB-01 (Rule 138E):-
GST Portal
shall not allow to generate E-Way Bill for following reasons.
1.
Composite Dealer have not file CMP-08 for two
consecutive Quarters.
2.
Normal Dealer failed to file Form 3B for
Consecutive Two Tax Period OR failed to file GSTR-1 for two Months or Quarters.
3.
Whose registration has been suspended.
However Registered Person may allow to
make application in FORM GST EWB-05 along
with reason to allow him to generate E-Way Bill.
Officer may allow him to generate
E-Way Bill and pass order in FORM GST EWB-06.
FORM FOR E-WAY BILL.:-
For Outward:-
TRANSACTION TYPE:-
Outward:- Causing outwards movement of goods for supply
or other than supply.
Inward:- Causing inward movement of goods for supply or other than supply.
REASON FOR TRANSPORTATION (SUB TYPE):-
Supply:- In case of outward supply of goods, the
supply liable to GST as per Schedule I or inward supply of goods liable to tax
under reverse charge by a taxable person.
Export or Import:- In case of export of goods from or
import of goods into the territory of India
Job Work:- When the principal and the job worker are
registered persons the EWB will be generated by the principal when he occasions
the movement of goods for job work and by the job worker when he occasions the
movement after job work, and by the recipient, if job worker is not a
registered person.
SKD or CKD:- The goods may be supplied on semi knocked
down (SKD) condition or the goods may be supplied in batches to be assembled at
the place of recipient in case of completely knocked down (CKD) conditions, the
e-way bill is to be generated, based on the value of the product being
transported.
Line Sales:- When
the goods are taken in the delivery van in a particular route to effect sale to
all the retailers, the movement of goods is to be covered by an e-way bill. When
the goods are moved under ‘Recipient not known’, they may not know the details of
sales. However the total value of consignment e-way bill has to be generated.
Sales Return:- When the recipient rejects and sends back the
goods they have to generate e-way bill or the supplier will have to generate
e-way bill on the capacity of the recipient of such goods.
Exhibition or Fairs:- When the registered person is going
to participate in any exhibition or fair, and the goods are moved from the
godown of such person, then e-way bill is to be generated.
For own use:- When goods are purchased for personal use,
the supplier will generate EWB.
Others:- For any item other than the above, such as
movement of goods for provision of supply of service or for any other purpose which
involves movement of goods, EWB should be generated.
Offence:- Contravention of Sections or Rules.
Notice:- Issue Notice within 7 days of such detention & Pass order for penalty within 7 Days of service of Notice.
Penalties:-
·
Owner of the goods comes forward for payment
of such penalty.
1.
For Taxable Goods:- 200% of
Tax Payable or 50,000/- Whichever is Less.
2. For Exempted Good:- 2% of Value of Goods or 50,000/- Whichever is Less.
·
Owner of the goods does not come forward for
payment of such penalty.
1.
For Taxable Goods:- 50% of
Value of Goods or 200% of Tax Payable Whichever is Higher.
2. For Exempted Goods:- 5% of Value of Goods or 50,000/- Whichever is Less.
Time limit for Payment of Penalty:- Within 15
days of order, otherwise the goods or conveyance so detained or seized shall be
liable to be sold or disposed of.
Release of Vehicle:- On Payment of Penalty specify above or
1 Lakh Rupee Whichever is Less.
Important FAQs:-
Q:- I am dealer in tractors. I purchased 20
tractors from the manufacturer. These tractors are not brought on any motorized
conveyance as goods but are brought to my premise by driving them. Also, these
tractors have not got the vehicle number. Is e-way bill required in such cases?
A:- E-way bill is required in such cases. The
temporary number or any identifiable number with the tractor have to be used
for filling details of the vehicle number for the purpose of e-way bill
generation.
Q:- What should be the value in e-way bill in
case goods are sent on lease basis as the value of machine is much higher than
leasing charges?
A:- The value of goods needs to be mentioned as
per the explanation 2 of the sub–rule (1) of rule 138.
Q:- Expired stock has no commercial value, but is
often transported back to the seller for statutory and regulatory requirements,
or for destruction by seller himself. What needs to be done for such cases of
transportation of the expired stock?
A:- E-way bills are required to be generated even
in cases where goods are moved for reasons other than supply. Delivery Challan
is the basis for generation of e-way bill in such cases.
Q:- Whether shipping charges charged by
E-commerce companies needs to be included in ‘consignment value’ though the
same is not mentioned on merchant’s invoice?
A:- Consignment value of goods would be the value
determined in accordance with the provisions of section 15. It will also
include the central tax, State or Union territory tax, integrated tax and cess
charged, if any. So shipping charges charged by the e-commerce companies need
not be included in the ‘consignment value’.
Q:- Where an invoice is in respect of both goods
and services, whether the consignment value should be based on the invoice
value (inclusive of value of services) or only on the value of goods. Further,
whether HSN wise details of service is also required to be captured in Part A
of the e-way bill in such case.
A:- Consignment value and HSN needs to be
determined for goods only and not for services as only the goods are in
movement and e-way bill needs to be generated accordingly.
Q:- How to generate the e-way bill for different
registered place of business?
A:- The registered person can generate the e-way
bill from his account from any registered place of business. However, he/she
needs to enter the address accordingly in the e-way bill.
Q:- How does taxpayer enter Part-A details and
generate e-way bill, when he/she is transporting goods himself/herself?
A:- Sometimes, taxpayer wants to move the goods
himself. E-way bill Portal expects the user to enter transporter ID or vehicle
number. So if he/she wants to move the goods himself/herself, he can enter
his/her GSTIN in the transporter Id field and generate Part-A Slip. This
indicates to the system that he/she is a transporter and he/she can enter
details in Part-B later when transportation details are available.
Q:- What has to be entered in GSTIN column, if
consignor or consignee is not having GSTIN?
A:- If the consignor or consignee is unregistered
taxpayer and not having GSTIN, then user has to enter ‘URP’ [Unregistered
Person] in corresponding GSTIN column.
Q:- Are e-way bills required to be issued for
imports and exports as well?
A:- Since imports and exports have been
considered as inter-state supplies under the GST act, the e-way bill is
required to be issued for these transactions as well. For imports, the e-way
bill will be generated by the importer. The exporter is liable to generate the
e-way bill for export supplies.
Q:- What has to be the shipping address in case
of export supply type?
A:- For Export supply type, the ‘Bill To’ Party
will be URP or GSTIN of SEZ Unit with state as ‘Other Country’ and shipping
address and PIN code will be of the location (airport/shipping yard/border
check post) from where the consignment is moving out from the country.
Q:- What has to be the Dispatching address in
case of Import supply type?
A:- For Import supply, the ‘Bill From’ Party will
be URP or GSTIN of SEZ Unit with state as ‘Other Country’ and dispatching
address and PIN code will be of the location (airport/shipping yard/border
check post) from where the consignment has entered the country.
Q:- How the distance has to be calculated, if the
consignments are imported from or exported to other country?
A:- The approximate distance for movement of
consignment from the source to destination has to be considered based on the
distance within the country. That is, in case of exports, the distance is taken
as the consignor's place to the place from where the consignment is leaving the
country, after customs clearance and in case of imports, the distance is taken
as the place where the consignment reached the country and was cleared by the
custom to the destination place.
Q:- Whether e-way bill is required, if the goods
are being purchased and moved by the consumer to his destination himself?
A:- Yes. As per the e-way bill rules, e-way bill
is required to be carried along with the goods at the time of transportation,
if the value is more than Rs. 50,000/-. Under this circumstance, the consumer
can get the e-way bill generated from the taxpayer or supplier, based on the
bill or invoice issued by him. The consumer can also enrol as citizen and
generate the e-way bill himself. For threshold limit of value of goods
intrastate movement for generation of E Way Bill, please refer to the relevant
statute/provisions passed by the respective States/Union Territories.
Q:- How to enter the vehicle number DL1A123 as
there is no format available for this in e-way bill system?
A:- If the RC book has vehicle number like
DL1A123, then you enter it as DL01A0123. The vehicle entered in the e-way bill
system is only for information and GST officer will accept this variation.
Q:- How to handle “Bill to” - “Ship to” invoice
in e-way bill system?
A:- Sometimes, the tax payer raises the bill to
somebody and sends the consignment to somebody else as per the business
requirements. There is a provision in the e-way bill system to handle this
situation. In the "Transaction Type"select the Bill to - Ship to
option in Transaction Type dropdown. Then the system will enable the "Ship
to" field for entering different state pin code for the Consignment.
Q:- How to handle “Bill from” - “Dispatch from”
invoice in e-way bill system?
A:- Sometimes, the supplier prepares the bill
from his business premises to consignee, but moves the consignment from some
others’ premises to the consignee as per the business requirements. This is
known as ‘Billing From’ and ‘Dispatching From’. E-way bill system has provision
for this in the "Transaction Type". Select the "Bill From -
Dispatch From" in Transaction Type dropdown, then system will enable the
Dispatch From field for entering different Dispatch state pin code for the
Consignment.
Q:- In case of Public transport, how to carry
e-way bill?
A:- In case of movement of goods by public transport,
e-way bill will be generated by the person who is causing the movement of the
goods. In case of any verification, the person can show e-way bill number to
the proper officer.




Comments
Post a Comment